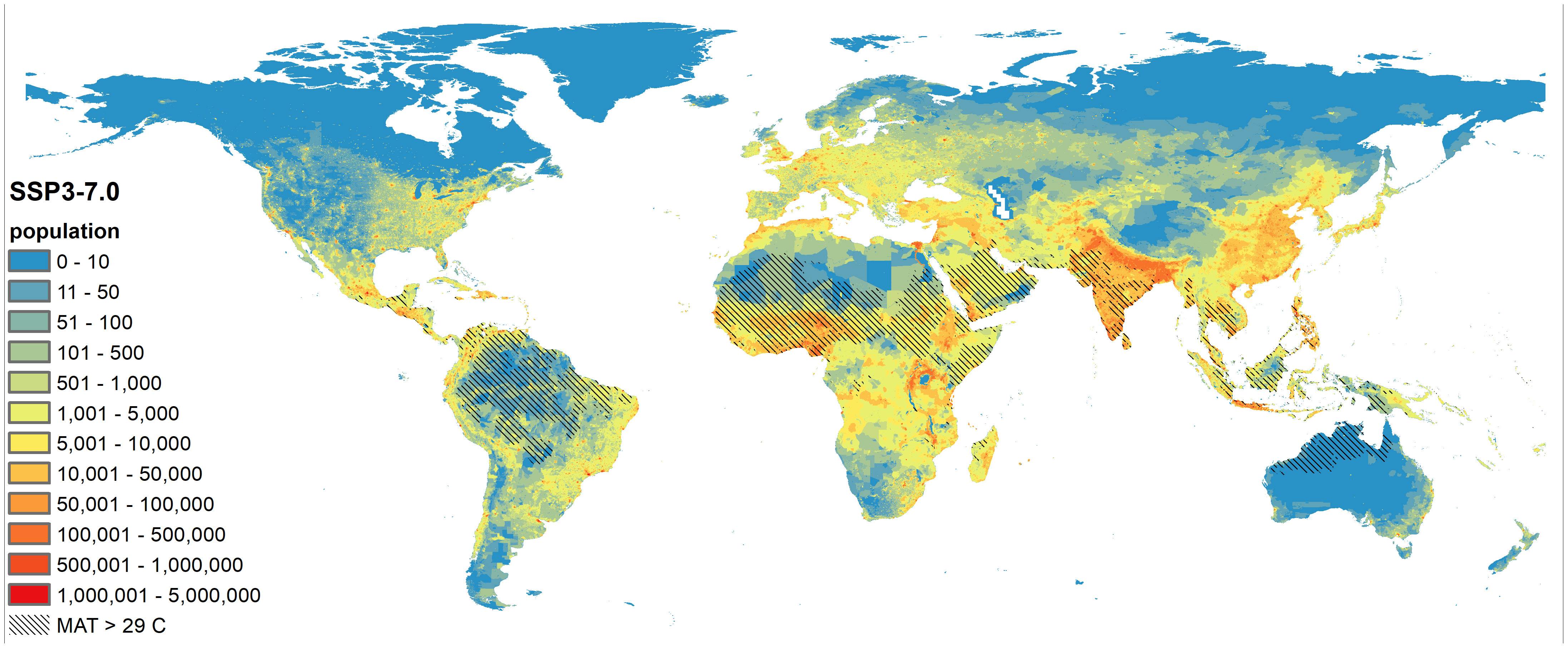
In recent years, there has been an increase in awareness about the dangers of climate changes. It's a critical global challenge that needs to be addressed by governments. The impacts of climate change could include the spread and increase of vector-borne diseases as well as rising sea levels. Climate change can also have devastating effects on cultural heritage and natural resources.
Indigenes make up one of the most vulnerable groups. In the policy discussions about climate changes, they are often neglected by the media. But their voices are essential to the dialog about this problem.

Incorporating their traditional knowledge into climate policies is an opportunity for Indigenous peoples to play a critical role in addressing the climate change issue. This step will help to develop more effective and sustainable adaptation strategies. Moreover, the inclusion of these groups in policy discussions and decision making can enhance their resilience to climate change.
Despite climate change being a pressing concern in international affairs, there are not many studies that study the impact of climate awareness on behavior. Research has shown that individuals' willingness to take action is not the only indicator of climate protection. Other factors like the environment and economics may also play an important role.
Many industrialized countries have not reduced emissions in line with Kyoto commitments. These countries are pointing out that these countries have not fulfilled their commitments. This is especially true for the Great Plains region. Although it could have a large wind resource, it also has problems with managing hydropower from the Missouri River.
Germany conducted a study to examine the effect of climate change awareness and behavior. It was found that 71% of respondents considered environmental protection to be the most significant threat. 66% thought climate change was the most serious threat. Therefore, it appears that individuals' climate change awareness has increased over the last three years.
Climate change awareness has also been heightened by social movements. For example the Fridays For Future campaign was started in August 2018. There were more than 49,000 events held in over 6300 cities throughout 215 countries. 8.6 Million people attended. Within three months, the movement had spread to Australia and Denmark.
Accordingly, the Conference of the Parties has reviewed the Parties’ commitments in light of the latest scientific findings and the Convention's goals.
UNEP's outreach programme aims to raise climate change awareness through educational and public awareness campaigns. This includes supporting the efforts of civil societies, providing additional tools, and encouraging youths take action on climatefriendly measures.
UNEP's outreach program aims to increase participation by young people in climate-friendly initiatives. To this end, the UNEP has co-sponsored regional workshops in Africa, Asia and Latin America. Through these workshops, the barriers to climate awareness were identified and the opportunities to overcome them were explored.
FAQ
What is the effect of climate change upon biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changes in extreme weather events and sea levels, as well as increased acidity in the ocean are just some of the issues affecting wildlife and ecosystems today.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Climate change is also causing rising temperatures and more extremes like droughts/floods. This adds to the stress already placed on fragile systems such coral reefs and tropical rainforests. Climate change could lead to the extermination of up to 30% of animal species by 2050. This would cause further ecological community losses.
Climate change poses a grave threat to biodiversity, but also to human societies that are dependent on functioning ecosystems to provide food, fresh water and timber. To mitigate its effect efforts must be made at all levels to reduce global warming trends and future damages should be avoided where possible with careful management practices.
How can extreme weather events be related to climate changes?
Global warming is directly connected to extreme weather events such a heat wave, floods or droughts, cyclones storms, hurricanes, and cyclones. Global warming has caused an increase in atmospheric temperatures. This has had an impact on different weather phenomena worldwide.
Climate scientists say that the average frequency of extreme weather-related disasters had more than doubled since 1980. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This affects the normal distribution of storms and hurricanes in different geographical regions across the planet.
The 2015 El Nino event brought warm water toward South America. It caused alarmingly high temperatures and heavy rains, which led to flooding in Peru. These floods resulted in displacement of people and property destruction. Several places including Antarctica have recorded their highest-ever temperatures indicating a definite relation between global warming trends and the occurrence or frequency of extreme weather events around the world.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, (IPCC), concluded that human activities are increasing severity of climate change. This naturally leads, in turn, to more severe and intense natural disasters globally. Thus, there is strong evidence concerning humans' relationship to extreme weather events occurring around us all.
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Due to limited access, technology, and healthcare systems, developing countries, communities, are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. Changes in temperature and precipitation can put more pressure on already limited resources. This is accompanied by flooding and droughts that weaken already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields. This will impact communities with low incomes and food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
The long-term impacts of climate change include resource scarcity, poverty, increased health risks, and an increase of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever. Additionally, flooding will become more common due to rising sea levels and extreme weather. These risks can put lives at high risk in coastal areas with a dearth of infrastructure or emergency services. To build resilience against these risks, mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions is necessary. Other measures include improved management and better access to water resources.
What role does climate change play in greenhouse gas emissions?
Climate change is driven by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible layer around the Earth trapping infrared radiation. This warms the atmosphere. Without them, the planet would be much colder than it is today.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. These activities increase the heat that is trapped in the atmosphere. This leads to higher temperatures and more extreme weather events.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Climate change is also caused by major greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxides (N2O).
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. Global warming has caused an increase in temperature all around the globe, and in our oceans. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To reduce further damage caused by climate change, human beings need to decrease their greenhouse gas emissions. We can do this by shifting away from fossil fuels in favor of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These activities will reduce atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and create a healthier environment that supports all life.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce your Carbon Footprint and Fight Climate Change
There are many actions you can take in order to reduce your carbon emissions and fight climate change. First, invest in energy-efficient appliances and lighting. You can also save energy by unplugging electronics when not in use, using public transit, walking rather than driving, and turning down the temperature on your thermostat in the winter and summer months.
Second, recycling materials is a good idea. You can compost food scraps and not throw them away. For shade and natural cooling, consider planting trees around your home. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Additionally, look into purchasing products with minimal packaging.
In addition to reducing your own personal emissions, you can also support organizations that focus on reducing global emissions such as Emissions Reduction Alberta; Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute or The Nature Conservancy Canada work towards lowering emissions through clean energy investments and international initiatives like ICLEI - Local Governments for Sustainability's urban sustainability strategies program.
Everyday changes can be made to help fight climate change.