
The climate system has both positive and negative feedbacks. A key component of the climate system are the feedbacks. They counteract the effects caused by climate forcing. The change in radiative emissions is one common indicator of the effectiveness of a feedback. These measures are known as feedback parameters. These measures are useful when assessing the potential climate change resulting from a perturbation.
For example, the carbon climate feedback parameter g (carbon-climate feedback) is a measure the relative influence of a warming top on land carbon inventories. This measure is important because it measures the extent to which warmer climates alter the land's carbon content. It is not an exhaustive measure of climate feedback.
Similarly, the carbon-concentration feedback parameter (b) represents the extent to which a rising atmospheric CO2 concentration enhances the uptake of CO2 by the ocean. Unlike the carbon-climate feedback, b is a function of both land and ocean CO2, but the magnitude of b is smaller when the CO2 concentration is greater.
Sea ice and cloud feedbacks are other examples of feedbacks. Both of these processes affect the polar regions. Although they are less important in the polar regions than in the tropics due to their weaker effects, they are nonetheless vital. These interactions can be simulated by climate models. These processes can also be estimated using observations.
The largest water vapour-related feedbacks are found in the tropical tropics. A rise in water vapor helps to increase the initial heat flow. Water vapour increases the greenhouse effect and thus further warms the planet. A rise in water vapor causes ocean warming. These feedbacks have been examined in detail for geological phenomena.
The ice-ocean heat store feedback is a very small measure of the effects of climate change on thermal energy storage. This is a sensible measurement as heat lost increases the amount of heat that is stored. This effect can be quantified in a variety of ways, which can help us understand the mechanisms behind climate change.

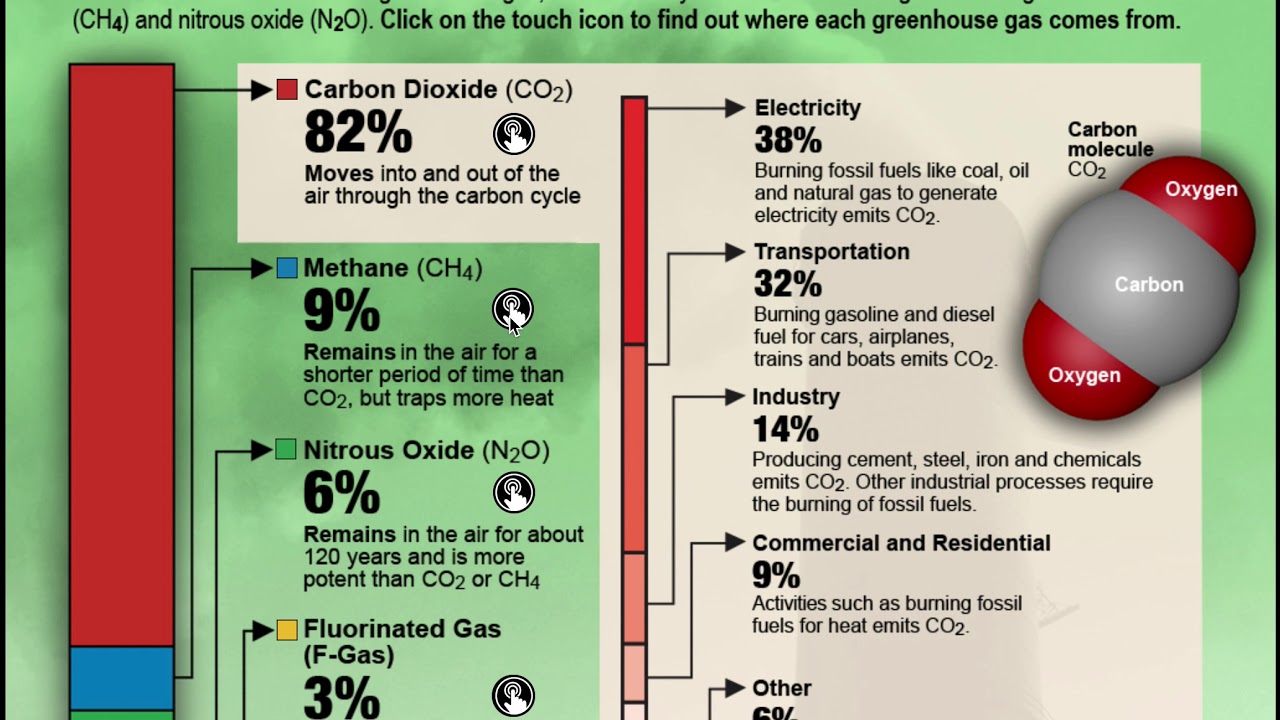
The climate system also includes carbon-cycle feedbacks. They are directly related to changes in land- and ocean carbon inventories. Generally, these parameters are diagnosed by comparing differences in model simulations constrained by observations. These parameters should not be compared for the exact same scenario. However, there are significant differences in model outputs and uncertainties that can be quite large.
The best estimates for total feedback range from two to five K. They are not perfect but are close. These calculations show that the equilibrium temperature change for the most well-known example is around 2.9 K. Adding 3.5 W m-2 more CO2, the expected equilibrium temperatures changes range from 2-5.8 K. Thus, the standard radiative Feedback framework is an acceptable approximation. These parameters must be adjusted to include non-radiative feedbacks like ocean evaporation or condensation.
FAQ
How do climate change and global warming impact agriculture and food security?
Global warming and climate change have an immediate impact on agriculture and food safety. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can cause disruptions in farming, decrease crop yields, and result in a loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures may lead to an increase in pests and diseases that can affect crops. They can also result in shifts of ranges suitable to agricultural production. This can lead to higher food costs and worsening nutrition.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. Climate change can also impact livestock production. Warm summer temperatures can reduce the fertility of animals like cows, sheep, and goats. This can cause lower milk yields and increase food insecurity within communities.
Although the relationship between climate change, global warming, and other factors is complex, there are efforts being made by governments to mitigate them through adaptation strategies. These include strategic investments in climate smart agriculture (CSA), which allows governments around the globe to make strategic investments in adapting their agricultural systems. This means promoting sustainable methods, such as crop rotation and the preservation of native seed varieties. These strategies help prevent adverse effects from climate change or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
It is essential that farmers worldwide adopt technologies that are more responsive to changes in the environment when selecting the right crops to grow on specific parcels of land to ensure food security amid a rapidly changing environment. It is essential to make improvements in existing infrastructure so that appropriate actions may be taken when crucial crop thresholds are reached. This includes the introduction of stable irrigation networks with adequate access waters at times when there is less availability due to warmer temperatures or heavy downpours, which can wash away important access water resources. To truly create lasting solutions that ensure continued adherence to international dietary guidelines regarding quality nutrition within our increasingly variable climates all over the globe - cohesive collaboration between stakeholders ranging from various government administrations at an international level right down to NGOs at local community sites is required.
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Global warming directly links extreme weather events like heat waves, floods. droughts. cyclones. storms. Global warming has caused an increase in atmospheric temperatures. This has had an impact on different weather phenomena worldwide.
According to climate scientists, the frequency of extreme weather-related catastrophes has more than doubled in the past 20 years. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This impacts the normal distribution of storms or hurricanes in different areas across the globe.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Many places, including Antarctica, have experienced their highest temperatures ever. This indicates a direct relationship between global warming trends as well as the frequency or occurrence of extreme weather events all over the globe.
Another example of climate change at work is Hurricane Irma. It was a major storm that struck Florida in 2017, causing economic losses of $50 billion.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, (IPCC), concluded that human activities are increasing severity of climate change. This naturally leads, in turn, to more severe and intense natural disasters globally. Thus, there is strong evidence concerning humans' relationship to extreme weather events occurring around us all.
What can be done to reduce or mitigate the effects of climate change?
There are many things you can do to lessen and mitigate the consequences of climate changes. These include reducing greenhouse gas emission through more energy efficient practices and using other sources of energy, improving land management practices, protecting forests, wilderness habitats, and protecting against extreme weather events like floods and droughts. Additionally increasing public education about climate change is also important as it encourages people to feel responsible for their actions.
How can the world work towards a more sustainable future when faced with the challenges of climate change?
Sustainability is the ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. We must take urgent action to reduce our dependency on finite resources and adopt a more sustainable way of using them.
In order to create a more sustainable world, we must change our consumption patterns and production methods. We also need to consider our dependence on natural resources, such as fossil fuels. We must seek out new technologies, renewable sources of energy, and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our everyday needs.
It is important to adopt an integrated approach to sustainability. This includes considering all aspects, such as the materials used and waste management. It also means incorporating energy utilization in transportation, industry, and industry. There are many solutions that can be found, such as the utilization of renewable energy, like solar, winds, and hydropower, better waste management, higher efficiency in agriculture, improved transportation networks, green building regulations and sustainable urban planning.
Furthermore, behavioral changes are required amongst individuals across different sectors throughout society for us to accomplish this goal. Education programs are required to educate people about climate change and show them how they can help create a more sustainable future.
In the end, it is only through collaboration between industry leaders and citizens that we can make significant progress in creating more sustainable worlds for future generations.
What are the current international efforts to combat climate change?
International efforts to combat climate change are moving at a remarkable pace and with unprecedented unity. Countries all over the world are now working together to reduce emissions, improve resilience against impacts, as well as invest in renewable energy sources.
The Paris Agreement has energized collective action at the global level and is a framework that allows individual countries to set voluntary emissions reduction targets. Additionally, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is providing political guidance and piloting new initiatives such as carbon market mechanisms.
Other regions are seeing progress. The European Green Deal is a comprehensive legislation package that seeks to create a European economy with sustainability as its core. Countries on the African continent also have committed to The African Renewable Energy Initiative, which aims increase Africa's participation in global renewable energy production.
Along with policy changes, action can be observed across all sectors and industries. Cities are actively moving toward sustainable public transport systems. Society as a whole is moving towards more sustainable lifestyles. Companies invent technologies that reduce carbon emissions. Investors are shifting their capital away to renewables.
The OECD committee's wealthy members have adopted common standards in reporting on national actions related to climate change. These are the Common Reporting Frameworks (CFR), also known as the 2021 Guidelines.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to make Your Home more Energy-Efficient and Reduce Climate Change
It is possible to make your home more energy efficient, reduce your carbon footprint and save money on your utility bills.
Make sure your home is well insulated and sealed. Check for drafts, ensure doors and windows are properly installed, and then seal any gaps or cracks with caulking.
Insulate your walls, ceilings, and floors to maximize energy efficiency. You should inspect your attic and other areas for leaks.
Lighting accounts for up to 18% of total household electricity usage so make sure you switch to LED light bulbs which use up to 80% less electricity than traditional incandescent ones! You can also save money by installing motion sensors and timers to turn off lights when they are not needed.
An old boiler or furnace can be replaced to save money on energy. They are also more efficient. You might consider a programmable thermostat, which allows you set the temperature according to when someone is at home or away.
Double-glazing windows can be replaced with better insulation. They also prevent heat from escaping through the glass. Low-flow showerheads are a great option, as they reduce water consumption but maintain adequate pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated appliances are more efficient than non-certified models and can use as much as 50% less power. Don't forget about small details such as unplugging electronic devices like phone chargers or TV boxes when not in use - this could save you a significant amount of energy over time!
These few simple steps will make your home more energy efficient and reduce your carbon footprint.