
A heat wave that decimated hundreds of people in the Pacific Northwest Region of the United States killed hundreds during the summer of 2021. It was caused in part by a high pressure area that remained over the region several weeks. This weather pattern caused several wildfires.
During the same period, extreme heat hit South Asia, killing 90 people in India and Pakistan. It contributed to floods in Pakistan due to the melting of a glacier. These events can be attributed to climate change, which has changed the wind patterns. Jet stream is a fast-moving, air current that travels from west to east and can lead to heat waves. As climate change changes the air patterns, these extreme heat events may become more frequent. As the heat is more intense, society will be affected.

There is evidence to suggest that climate change may be causing heat domes, which trap warm atmosphere on the Earth's surface. These conditions can be exacerbated by high pressure systems and dry soils. The ground is more susceptible to heat if it's dry. High pressure forces the warm air towards the earth.
Heatwaves pose a threat to human lives and are one of the most prevalent natural hazards. They can cause heat-related illnesses, blood clots, and dehydration. Among other impacts, they contribute to the spread of wildfires in areas where drought conditions are prevalent.
According to climate experts and scientists, the frequency of extreme events has increased as a result of human-induced global warming. Climate experts predict that the risk for heatwaves will rise by at least five degrees Celsius over the next century if the climate change effects continue. However, there are increasing trends in extreme weather that could make estimates less conservative.
Experts and researchers are working together to discover the causes of heat waves and how future climate change might affect them. Studies have shown that the combination of high pressure and dry soils can lead to an increased risk of heatwaves.
Heatwaves can last days, or even weeks. There are many dangers associated with them. People who have chronic conditions or are dependent on medication are more at risk of complications in a heatwave. Children are at greatest risk. In addition, heatwaves have been shown to cause the death of livestock and crops.
Many climate scientists estimate that the chance of heat waves having occurred 30 times more often since 1950s. They also expect that they will increase in intensity as well as length. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the likelihood of a heatwave in the U.S. has increased from three to seven percent per decade.
A recent study by Columbia researchers concluded that the heat dome of the Pacific Northwest was caused by a combination of anomalously dry soils, high pressure systems, and disruptions in the jet stream. It had a cascading effect that made the entire area extremely hot.
FAQ
What is climate Change and how does this happen?
Climate change is the long term shift in global weather patterns resulting from an increase of greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat, causing global temperatures to rise which leads to an array of changes in weather and climate. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
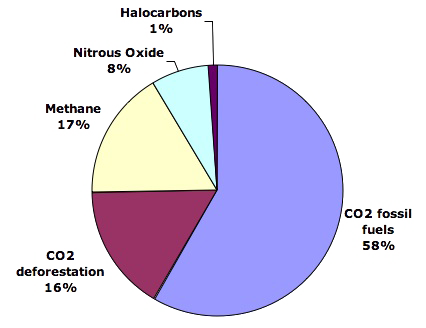
Global greenhouse gas emissions are also influenced by deforestation, which contributes about 15-20%. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Forests are also a natural carbon-sink that removes carbon dioxide from the air. Without this absorption capacity, carbon levels will continue increasing with devastating consequences for the ecosystems around the globe.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). While methane is used extensively in industrial processes, it contributes substantially to atmospheric heating. N2O comes primarily from soil management activities like fertilization and tilling that release excess nitrogen into the soil. This leads to N2O being produced upon microbial interaction.
To limit climate change, we must collaborate across economic, political, and social institutions in order to reduce our emissions and transition away fossil fuel dependence towards renewable energy sources. Replacing technologies that use polluting fossil fuels with smart solutions that promote zero-waste living could be an effective approach to decreasing atmospheric contamination while simultaneously reducing heating due to CO2 accumulation. Our environmental impacts can be reduced by adopting preservation measures like reforestation. These projects help to preserve biodiversity and absorb large amounts CO2 from the environment. This helps in addressing climate change and restoring balance for future generation.
What are some solutions to climate changes? And how effective do they work?
Climate change is an urgent issue, and it requires immediate attention from government, business, and citizens. The signs of a disturbed climate system include rising temperatures, extreme weather and sea level rises, as well as melting polarice. To attempt to tackle this phenomenon, multiple proposed solutions have been put forward ranging from technological solutions, and behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological solutions: A wide range of technologies have been used to address climate change. These include renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power which provide reliable sources of clean energy with minimal side effects on the environment. Electric cars powered entirely by renewable energy could replace petrol vehicles and significantly reduce pollution. Reforestation projects are another technological option that aim to increase carbon sequestration, soil and trees. They also provide coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable areas from rising ocean levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. So, for example, buying locally-produced goods reduces the transport costs associated with food transport. The use of public or active transportation, as well as reducing cost and air polluting simultaneously, is a good option. In the same way, better insulation in your home can help reduce dependence on gas boilers that heat your homes.
Geo-engineering (GEO): This involves large-scale interventions into natural systems that may be too risky because of potentially unforeseeable consequences.
The effectiveness of these solutions largely depends on how much producers commit themselves towards investing in green alternatives; currently, initiatives such as using electric Cars tend expensive when compared with petrol versions however economic incentives favoring green investments play an integral role in incentivizing alternative solution uptake otherwise these remain mostly dormant when exposed only market forces which cannot guarantee their utility over time try apart from increasing consumer awareness over time regarding their efficiency hence mandating alternative solutions via policy measures represents one way forward however this needs regulatory bodies willing committed enough engaging players involved further still nontechnological approaches work one level but solving global warming phenomena requires all parties involved tackling issue earnest together.
What are the ways climate change can be mitigated or reduced?
There are many steps that can be taken in order to reduce and mitigate climate change's effects. These include reducing greenhouse emissions by using greener energy sources and better energy practices. It's important that people are educated about climate change. This encourages them to take responsibility for their actions.
What are the impact of deforestation and land use change on climate change?
Deforestation, land use change and other factors have an immediate and direct impact on climate. Trees that are cut down or burnt can no longer absorb carbon dioxide. This is one of the most important greenhouse gasses on Earth. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
Changes in land usage can also cause more greenhouse gasses to be released into the atmosphere. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. Clearing can also increase soils with high levels of carbon stored in them; these soils can be disturbed or turned over by farming activities and release more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Deforestation and land-use changes can have a significant impact on regional air quality. As an example, deforestation smoke has been shown to reduce visibility and cause respiratory illnesses such asthma and other conditions. The cumulative effects of these changes in local air quality could have an impact on global climate change. Higher temperatures can be caused by more sunlight reaching the Earth's surface due to lower aerosol particles.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
What is the effect of climate change upon biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change is having a wide range of effects on biodiversity as well as ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changes in extreme weather events and sea levels, as well as increased acidity in the ocean are just some of the issues affecting wildlife and ecosystems today.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. A climate change scenario could see up to 30% loss of animal species by 2050. That would trigger a chain reaction of losses within eco-systems.
Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity and human societies, as well as to ecosystems that provide food, water, timber, or other services. You can mitigate the effects of climate change at all levels by reducing global warming trends. Further, future damages can be prevented with good management practices.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Carbon Footprint, Fight Climate Change
You can reduce your carbon footprint while helping to combat climate change by taking several steps. First, you can reduce your energy consumption by purchasing energy-efficient appliances, lighting and insulation. It is possible to save energy by not using electronics, taking public transit, walking or driving and setting the thermostat lower in the winter and the summer.
Second, recycle as much material as possible. Compost food scraps rather than throwing them away. This will ensure that they don't end-up in landfills which release methane gas into our atmosphere. Third, plants trees around your house for shade and natural cooling. The air absorbs carbon dioxide through the vegetation. Additionally, look into purchasing products with minimal packaging.
You can help reduce your personal emissions by supporting organizations such as Emissions Reduction Alberta, Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute and The Nature Conservancy Canada. These organizations work to lower emissions through clean energy investments. They also support international initiatives such ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability's Urban Sustainability Strategies program.
By making small changes within our everyday lives we can all contribute to fighting climate change together!