
A new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has detailed described the impact of climate change on planet Earth. The report found that global temperatures must remain below 1.5 degrees Celsius (C) in order to avoid serious consequences.
The report highlights five major risks. These are heat, droughts, coastal flooding storm surges, and sea level rise. Below is the "burning firecrackers" chart which shows the severity of risks at various levels. Darker colors indicate greater stress levels.
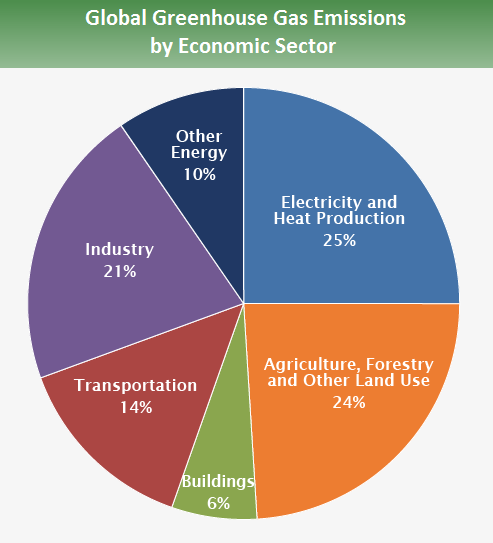
In addition to the physical effects of warming, there are also socioeconomic impacts. Increased risk of flooding and tropical cyclone surges will cause more people to be forced from their homes. This will increase deaths caused by extreme climate events. According to the report, the number of people at risk from coastal climate hazards will increase to one billion by 2050.
Many of the consequences of climate change are already evident, however, the report states that these impacts are greater than previously estimated. Many species have had the necessity to move their ranges in order to survive. Around half of land animals, and half of plants, have done so.
Climate change has caused significant changes in the ecosystems and also had devastating impacts on water access. Millions are currently experiencing food insecurity due to climate change. Additionally, increasing temperatures and storminess are reducing the availability of water resources. A number of natural disasters have also caused more than 8,000,000 people to be evacuated around the globe.
Eight percent of terrestrial species face extinction. This figure is predicted to rise to 13 percent at three degrees and to 15 percent at four degrees. The risk of regional extinctions is also increasing.

Increasing sea level will make flooding worse and could result in major cities losing their water resources. At the same, the oceans are warming which could lead to hypoxia. This will make marine microbes less able to absorb oxygen. Further, more greenhouse gases will be released into the atmosphere by the melting Arctic permafrost.
A key threat to agricultural production is drought. At two degrees, agricultural drought is projected to be 150 to 200% more likely. A decrease of 5 to 10% is expected in the yields of agricultural crops. It could result in the loss of vital nutrients such as zinc, depending on how much carbon dioxide is released into our atmosphere.
Other effects of climate change include changes to the amount of iron and zinc as well as protein and other nutrients. According to one study, a carbon-equivalent increase of atmospheric CO2 will decrease zinc by 77%. The same goes for protein. A CO2 equivalent increase will reduce it by 4%.
These conclusions are based off climate data from five different global climate models. They are compared with two scenarios of emission: a low scenario, and a high scenario. Each option outlines different approaches to reaching macro-level conditions before 2030.
FAQ
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, humans have contributed more than 70% of global warming since mid-20th century.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This increases the already high levels of atmospheric CO2, which acts as a greenhouse gas by trapping heat from Earth's sun and increasing temperatures. As Arctic ice melts, this causes ocean levels to rise and can cause severe weather patterns all over the globe, including floods, droughts and storms that could lead to food shortages.
Deforestation. Trees that absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in photosynthesis will be effected by being cut down. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. Deforestation is also associated with respiratory problems and local air quality.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
In conclusion, human activity has been drastically impacting our environment for centuries now, but with rapid advances made in technology such as renewable energy sources availability we have started turning our heads towards the future leaving behind carbon-emitting heavy industries results will soon start speaking themselves clearly when we leverage on technology through green innovation paving away toward eco-friendly efforts combatting climate change efficiently keeping everyone safe under prosperous nature purview.
What is climate Change and how does this happen?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
Human activity is the main factor in climate change. This includes burning fossil fuels to generate electricity and transport, cutting down forests and raising livestock. This is because these activities release huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It warms the planet faster than natural processes like volcano eruptions.
Deforestation also plays a large role contributing about 15-20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Additionally, forests act a natural carbon source that absorbs CO2 into the atmosphere. Without this capacity, carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will continue to rise with devastating effects for ecosystems around world.
Other than CO2, human-caused pollutants also release other dangerous gases such as methane and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere. Methane has been extensively employed in industrial processes. It contributes significantly to the atmosphere's warming. While N2O can be emitted primarily by agricultural soil management activities, such as tilling or fertilization which release excess nitrogen to soil.
To limit climate change, we must collaborate across economic, political, and social institutions in order to reduce our emissions and transition away fossil fuel dependence towards renewable energy sources. The smart solution to reduce CO2 accumulation and atmospheric pollution could be replacing polluting fossil energy sources with zero-waste solutions. By taking responsibility for our impact on our environment we can begin mitigating damage through preservation measures like reforestation projects which help maintain biodiversity while absorbing large volumes of damaging CO2 back into nature providing powerful assistance in addressing the climate crisis and restoring balance for future generations
How can the world make a transition to a more sustainable future given the challenges presented by climate change?
Sustainability is the ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. An urgent need exists to act to eliminate our dependency on finite natural resources and to shift towards a more sustainable method of using them.
For a more sustainable future it is essential to rethink our current consumption and production models, as we also need to reduce our dependence upon natural resources such fossil fuels. We must find new technologies, renewable resources of energy and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our daily needs.
Furthermore, it is crucial to take a holistic approach to sustainability. This includes considering all aspects, such as the materials used and waste management. It also means incorporating energy utilization in transportation, industry, and industry. There are many solutions that can be found, such as the utilization of renewable energy, like solar, winds, and hydropower, better waste management, higher efficiency in agriculture, improved transportation networks, green building regulations and sustainable urban planning.
To achieve this goal, we need to make behavioral changes in order for people from all walks of society to be successful. Education programs are needed which will support people in understanding the issues related to climate change and how they can contribute positively towards a more sustainable world through micro-actions such as reducing food waste or adopting low-carbon lifestyles.
In the end, it is only through collaboration between industry leaders and citizens that we can make significant progress in creating more sustainable worlds for future generations.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
Greenhouse gases are a key factor in climate change. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, the Earth would be much colder today than it is today.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. As more heat enters the atmosphere from these activities, it leads to increased temperatures and extreme weather.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Important contributors are also methane and nitrousoxide (N2O), as well fluorinated gases (Fgases).
The concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly since preindustrial times due to human activities. This has led both to global warming and an increase worldwide in temperatures, as well as increased ocean levels. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To reduce further damage caused by climate change, human beings need to decrease their greenhouse gas emissions. We can do this by shifting away from fossil fuels in favor of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. We can also take measures such as reforestation or adopting agricultural methods that allow the soil to absorb more CO2 from the air. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What impact does politics have on global efforts to tackle climate change?
Climate change is a controversial issue that has caused a lot of division between nations, governments and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has become increasingly difficult to come to an agreement on how to address this urgent environmental crisis globally.
Most scientists agree that humans are causing climate change. This is why it is urgent to act. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Many governments in the world want to protect their economic interests, and enforce measures that limit business activities. This often conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend to address climate change efficiently. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
It is difficult to reach a consensus about how to address climate change because of differences in power dynamics between countries. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. A number of potential side effects that could be caused by radical changes like geoengineering were also discussed at national and international levels.
In the same way, grassroots movements are fighting powerful opponents at the grassroots level. These include corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbyists looking to retain politically favorable positions.
It is essential to distribute resources properly to any intervention program, and to be mindful of political divisions within nations, if we want to see an effective coordinated effort to mitigate our current environmental crisis.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Educate Your Communities About Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Many forms of climate education are available, including interactive educational tools and online resources, as well as classroom activities, simulations, or experiential learning programs. These are the key components of climate change education.
-
People with practical knowledge on the subject
-
Demonstrating that people can make a real difference.
-
Involving participants in an open dialog about potential solutions
-
Inspiration through shared experiences that inspire action
Teachers can assist their communities in reducing their environmental footprint by teaching them comprehensive lessons about climate change.
Furthermore, connecting scientific research to real-world examples is a great way to engage audiences in a meaningful conversation. Exploring case studies and best practices also provides participants with opportunities to witness positive outcomes firsthand, which can inspire further innovation or replicable measures within their own communities or organizations.
By incorporating action-oriented activities into education curriculums, participants are equipped with the mental tools necessary to create campaigns or petitions. They can then become agents of change in their communities or for sustainability. Individual agency is important because it highlights the importance to reduce emissions. Participants can also be shown how they contribute collectively towards a better outcome. Involving stakeholders early in the decision-making process encourages them to be involved. This could lead to more equitable outcomes for all those affected by policy design decisions. By combining our efforts to raise public awareness about the impact of climate change with appropriate actions to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, we may be able create an environment in which these urgent matters are addressed with special attention where it is most needed. This will allow us to work together to implement successful measures that will help us achieve our collective goals.