
As the population of the world continues to increase, so too does the demand for food. Nevertheless, the world faces several challenges to food security. These include fast food transitions, high prices, overconsumption, inefficient supply chains, and increased prices. Climate change is also likely to have an impact on food production and distribution as well as consumer consumption. There are many options to reduce and adapt to the impact of climate change.

For example, climate-smart agriculture practices can reduce emissions from livestock products. These strategies are useless without concerted action to decrease greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture practices. A global food system must be reformed to minimize net food system greenhouse gas emissions, promote responsible consumption, and encourage nutrition. It is important to establish effective data collection systems and build a robust emergency foods reserve.
In order to make agricultural practices more efficient and improve post-harvest processing and waste management, effective technology is essential. Scientists must also be able to better understand how dietary interventions can reduce food waste and promote the well-being of communities. The scientific community can play an important role in facilitating these activities. They can provide knowledge on how to effectively manage dietary interventions and the cost effectiveness of such initiatives.
The role of scientists is not limited to developing global knowledge systems about sustainability. This system would combine information on human population dynamics, ecosystem services and agricultural practices into one comprehensive system. This information is particularly useful for fostering the development a food system that can withstand sudden climate changes.
Furthermore, scientists have the ability to communicate and quantify the vulnerability of the agricultural sector to climate changes. They can encourage investment in agriculture by sharing information on the economic benefits associated with climate-smart agricultural techniques. This can also help to reduce some of the adverse effects of climate change on food safety. Scientists can also identify potential areas for greenhouse gas mitigation.
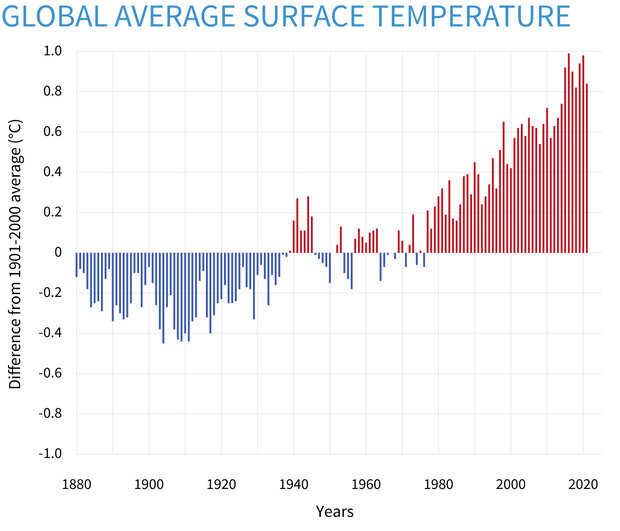
While scientists have much to contribute, a coordinated global response is a complex and multi-dimensional endeavor. In order to succeed, governments, private businesses, and civil society organizations must coordinate their efforts. Governments should work to ensure that policies are based on evidence, and that research is directed towards identifying the most practical policy solutions. To achieve this, governments should form common platforms, such as national and international climate change and food security committees. Public and private business alike should invest in sustainable, low-waste supply chain solutions.
Finally, the scientific community is able to support the development of a coherent, multidisciplinary understanding of food security. This understanding is crucial for the development of strategic and nimble investment strategies as well as evidence-based solutions to policy problems. Research should focus on the following areas: the most efficient dietary interventions; how to improve the nutritional quality of diets; the most effective methods of managing food losses; and the most cost-effective ways to reduce food waste.
FAQ
How can we address climate change by addressing the role of the energy industry?
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. Global warming can be caused by the burning fossil fuels. The atmosphere releases carbon dioxide, trapping heat and leads to an increase in Earth's temperature.
This requires energy sources to move away from carbon emitting sources like natural gas and coal, and instead shift towards renewable energy sources, such solar, wind, or geothermal. This shift can be made possible by both government policy and incentives as well investments in innovative technology like hydrogen-fuel cells. By investing in infrastructure that supports the use of these renewable sources, businesses and households can drive down emissions while simultaneously reducing their electricity bills.
Other options include switching away from petroleum-fueled cars, moving towards electric vehicles, and public transport. Governments can help lead society's transition from oil-based infrastructures to cleaner alternatives by funding research into battery technologies and encouraging consumers to make investments in cleaner modes.
Green business practices are essential to help reduce carbon emissions. Companies should implement better insulation systems in their offices, and energy efficiency plans in production facilities. This can help drastically reduce operational costs while simultaneously improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
What is climate Change and how does this happen?
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in global weather patterns that are caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing global temperatures to rise which leads to an array of changes in weather and climate. This could include rising seas, melting glaciers. extreme storms or droughts. Widespread coral reef bleaching.
Climate change is primarily caused by human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels for electricity, transportation, and cutting down forests. This is because these activities release huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It warms the planet faster than natural processes like volcano eruptions.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. It releases the stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when trees are chopped down or burned. Additionally, forests act a natural carbon source that absorbs CO2 into the atmosphere. Without this capacity, carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will continue to rise with devastating effects for ecosystems around world.
The release of CO2 into the atmosphere is not the only effect of human-caused polluting. Other harmful gasses like methane, CH4, and nitrous dioxide (N2O), are also emitted by humans. Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
To limit climate change, we must collaborate across economic, political, and social institutions in order to reduce our emissions and transition away fossil fuel dependence towards renewable energy sources. A smart approach to reducing atmospheric contamination and preventing CO2 accumulation could be to replace polluting fossil-fuel technologies with ones that encourage zero-waste living. Reforestation projects, which are powerful aid in the fight against climate change by absorbing large quantities of CO2 back into nature and maintaining biodiversity, can help us take responsibility for our environmental impact.
What are the most effective solutions for climate change?
Climate change is a pressing issue that requires urgent attention from citizens, governments, businesses, as well as citizens. A disrupted climate system is evident by rising temperatures, extreme weather events and increased sea levels. Numerous solutions have been suggested to deal with this phenomenon. They include technological solutions as well as behavioral changes and geoengineering.
Technological Solutions: An array of solutions have arisen to address climate change through changes in technology. These include renewable energy sources like solar power and wind power that provide reliable sources for clean energy while causing minimal harm to the environment. Electric cars powered by renewable energy could significantly reduce air pollution in cities by replacing petrol vehicles. Other technological solutions include reforestation programs that increase carbon sequestration in soil and trees, as well as coastal protection system to protect vulnerable locations from rising sea levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. For example, local production of goods and shorter supply chains can help reduce the emissions associated with transport costs. Using public or active transportation instead of personal cars also optimizes the use of resources and brings down cost and air pollution simultaneously; similarly opting for more efficient home insulation can reduce reliance on gas boilers for heating homes reducing emissions also lowering bills over time.
Geo-engineering is large-scale intervention in natural systems that are deemed too risky by potential unforeseen consequences. This includes widespread crop failures or depletion of fish populations. However, it is worth investigating because it could be more effective than human behavior at balancing current CO2 levels.
These solutions are only as effective as the producers who invest in green alternatives. Currently, electric Cars are more expensive than petrol models. However, economic incentives favoring green investments play an important role in incentivizing alternative solutions uptake. Market forces cannot guarantee their utility so they must be mandated via policy measures. This will require regulatory bodies to engage all players further. Nontechnological solutions work on one level while solving global warming requires everyone involved.
How do climate change and global warming impact agriculture and food security?
Climate change, global warming, and other factors have direct impacts on agriculture and food supply. Climate change can alter rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels and extreme weather. This can lead to disruptions in farming activities, lower crop yields, and loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can cause crop diseases and pests to multiply. It can also affect the ranges that are suitable for agricultural production. This can increase food production costs, as well as cause hunger and other nutritional problems worldwide.
Rising sea levels pose an additional threat, as they could inundate important agricultural land in many coastal regions, leading to increased salinity levels in wetlands where important crops are grown. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
Global warming and climate change have a complicated relationship. However, adaptation strategies are being implemented by governments globally through strategic investments made in climate-smart farming (CSA). This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. It is essential to make improvements in existing infrastructure so that appropriate actions may be taken when crucial crop thresholds are reached. This includes the introduction of stable irrigation networks with adequate access waters at times when there is less availability due to warmer temperatures or heavy downpours, which can wash away important access water resources. For sustainable solutions to be created that will ensure the continued compliance with international dietary guidelines in our ever-changing climates, it is necessary to have a cohesive collaboration among all stakeholders. This includes government officials at international levels as well as NGOs located at local communities.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes could have serious consequences for humans, causing instability in communities, intensifying poverty, insect-borne illnesses, changing human migration patterns, and destroying essential habitats.
Climate change is already having a wide range of sweeping effects on the environment and societies all over the world. As global temperatures rise, this trend is likely to intensify in the near term.
Global climate change has one of the most powerful effects on ocean levels. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Many countries are experiencing extreme weather events, such as droughts or heatwaves as a result climate change. These extreme weather events can cause widespread destruction of homes and businesses. In some cases, they lead to the displacement or relocation or even complete destruction of entire towns. Intense storms increase the risk of flooding and landslides. This can further damage infrastructure like roads, railways, and bridges.
Additionally, wildfires caused climate change are more common than ever. They can be devastating for both the habitats and the people who live nearby.
These drastic changes often lead to displacement or refugee crises. People move out of their homes involuntarily or voluntarily when their communities become unsafe or uninhabitable due to the altered climate.
An increase in aridity means that dust storms can occur more frequently, making people with asthma and other respiratory illnesses like asthma particularly vulnerable. In addition, pest infestations are expected to increase significantly linked with higher temperature extremes - a phenomenon known as 'greenhouse bug' - leading to further damage to agricultural production that further affects global food insecurity numbers as fewer crops become available at worse nutritional qualities potentially bringing additional hardships upon marginalized populations already barely able make ends meet otherwise.
Statistics
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Incorporate Sustainable Practices Into Your Daily Life To Fight Climate Change
One way you can incorporate sustainable practices into your daily life is by reducing your consumption of resources such as food, clothes, and energy. Try shopping secondhand, borrowing from family and friends, or buying new items every other day. A vegetarian diet once or twice a month can help to reduce the amount of methane that is released into the atmosphere by reducing livestock production. To conserve energy, it is a good idea to turn off all lights when you leave a room.
The other way to combat climate changes is to reduce carbon emissions from transportation such as cars and aircrafts. Renewable power sources, such as solar panels, can be used to replace traditional fossil fuels. It is crucial to support measures at the policy level that encourage clean air regulations in order to make climate change mitigation work. Finally, engaging with others around issues like ending plastic pollution and deforestation is hugely beneficial since it creates more conscious citizens who will act upon their knowledge!